Why No Distortion at the Top?
October 14, 2024Have you ever wondered, “Why No Distortion At The Top?” This seemingly simple question opens up a fascinating world of physics, engineering, and design. Whether you’re an aspiring architect, a curious mind, or simply intrigued by the structures around us, understanding the principles behind load distribution and structural integrity is key to appreciating the marvels of construction.
Load Distribution: The Unsung Hero of Stable Structures
The answer to why there’s no distortion at the top lies in a fundamental concept called load distribution. Imagine a stack of books; the weight of each book is distributed evenly among the books below it. Similarly, in a building or any structure, the load – which includes its own weight, occupants, furniture, and environmental factors like wind and snow – isn’t just concentrated at the top. It’s carefully distributed throughout the entire structure, from the topmost point down to the foundation.
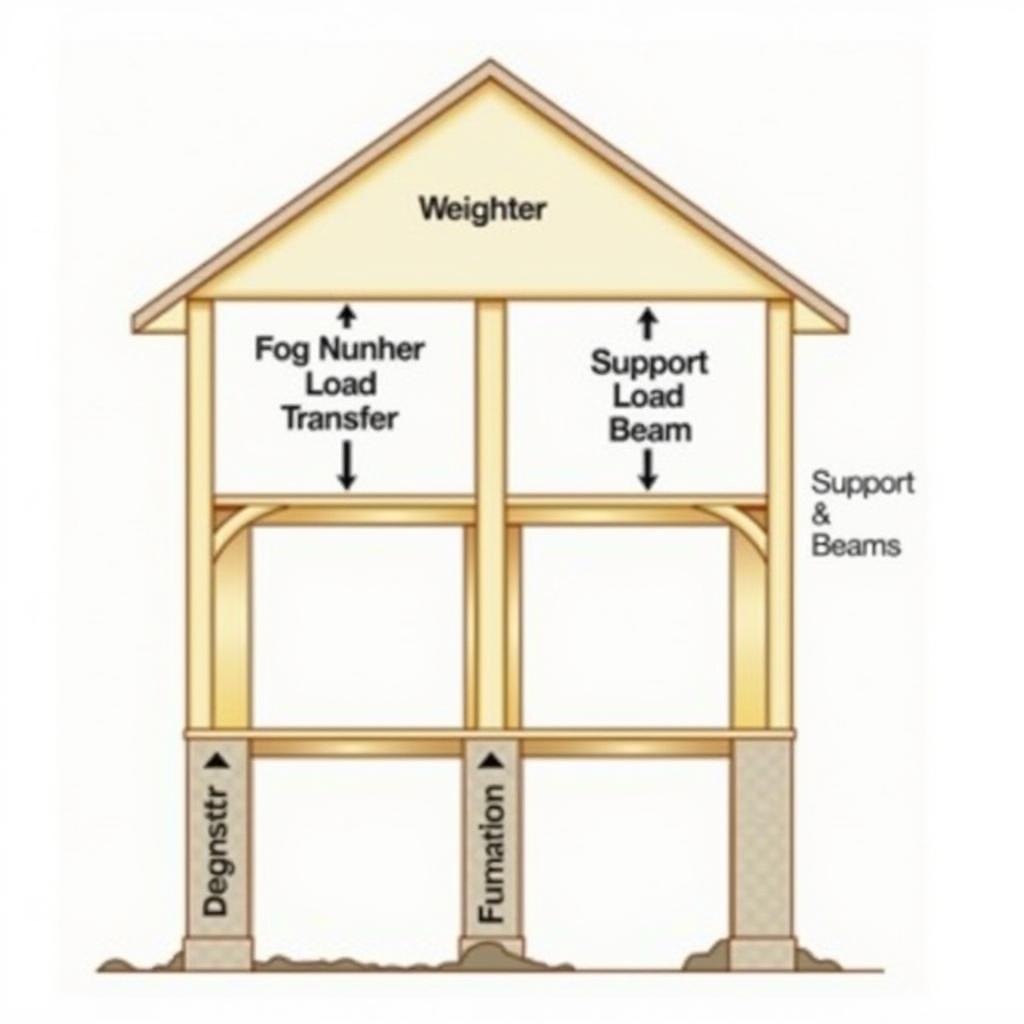 Load distribution in a building
Load distribution in a building
The Role of Strong Materials and Intelligent Design
Of course, load distribution wouldn’t be possible without strong materials and intelligent design. Architects and engineers meticulously select materials like steel, concrete, and wood based on their strength and ability to withstand specific loads. They then design the shape and structure of the building to ensure that these materials work together to distribute the load efficiently.
Think about the arches of a bridge. Their curved shape is not merely aesthetic; it’s a brilliant engineering solution to transfer the load from the bridge’s deck to its supports, preventing distortion at the top.
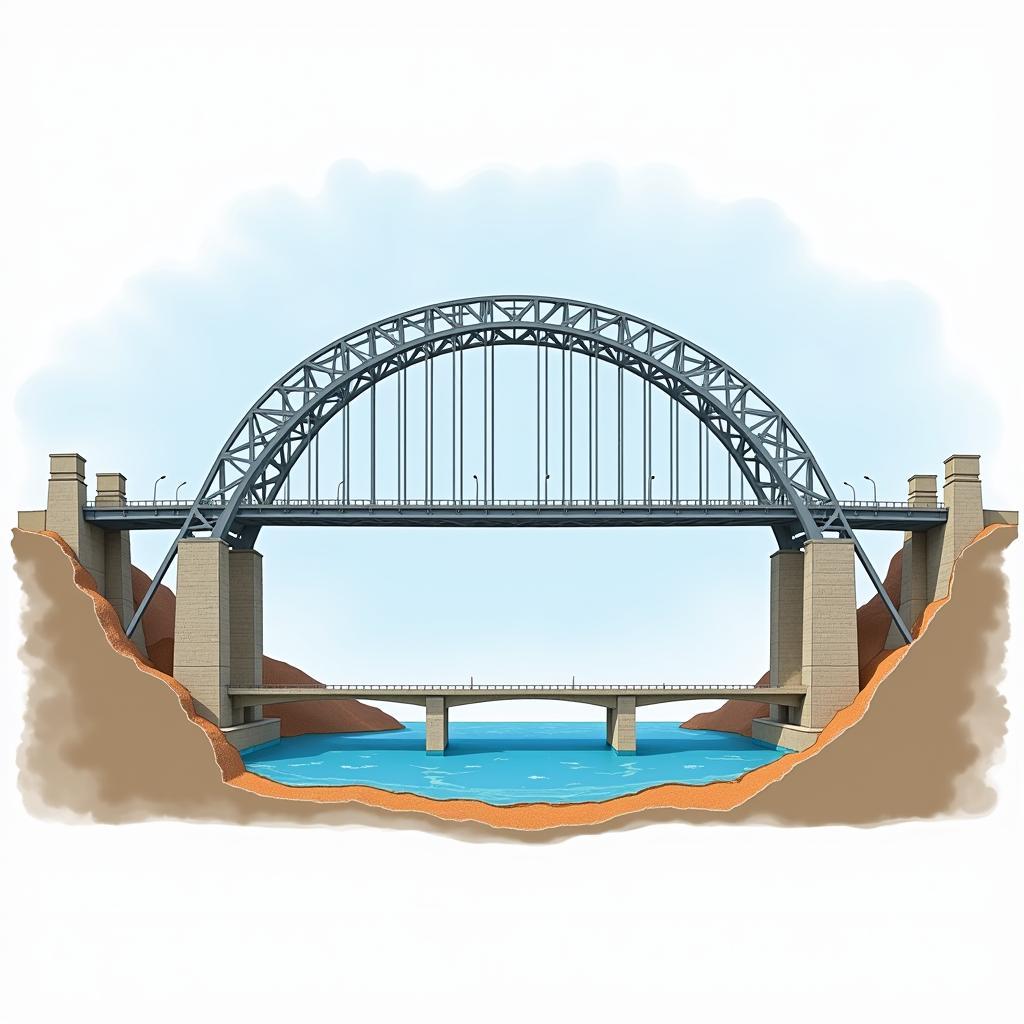 Load distribution in an arch bridge
Load distribution in an arch bridge
Ensuring Stability: A Multi-Faceted Approach
Achieving “no distortion at the top” isn’t a single-step process but rather a combination of factors:
- Strong Foundation: A stable foundation is crucial. It ensures that the load is transferred evenly to the ground, preventing the entire structure from sinking or tilting.
- Load-Bearing Walls and Columns: These vertical elements are strategically placed to carry the weight from the roof and upper floors down to the foundation.
- Beams and Trusses: Horizontal elements like beams and trusses help distribute the load across a wider area, preventing excessive stress on any single point.
- Geometric Shapes: Triangles, arches, and domes are inherently strong shapes that efficiently distribute loads, contributing to the overall stability of the structure.
Beyond Buildings: Load Distribution in Everyday Life
The principles of load distribution are everywhere! Consider a simple chair:
“The legs of a chair are designed to distribute your weight evenly to the floor,” explains Dr. Emily Carter, a structural engineer. “The backrest and seat further distribute the load, ensuring stability and preventing the chair from collapsing.”
Conclusion
So, why no distortion at the top? It’s a testament to the ingenuity of human engineering and the power of understanding fundamental physics principles. By carefully distributing loads, using strong materials, and employing intelligent design, we create structures that are not only visually impressive but also incredibly stable and safe. The next time you marvel at a skyscraper or walk across a bridge, take a moment to appreciate the invisible forces at play, working tirelessly to keep us grounded.